Navigating the complexities of molecular biology requires understanding essential tools like the pET28a plasmid map. This comprehensive guide explores what makes pET28a a cornerstone for recombinant protein production in E coli, detailing its key features and applications. Discover how this bacterial expression vector facilitates high-level protein synthesis, making it invaluable for researchers in various fields, from biochemistry to biotechnology. We delve into the critical components, including the T7 promoter and His-tag, explaining their roles in efficient protein purification and analysis. Understanding the pET28a plasmid map is crucial for anyone seeking to optimize their protein expression strategies and achieve successful experimental outcomes. Learn about its selectable markers, replication origin, and multiple cloning sites, which are all vital for effective cloning and expression workflows. This resource aims to provide clarity and practical insights into harnessing the full potential of pET28a for your scientific endeavors, offering a clear roadmap to successful protein expression and purification with this widely used vector.
Decoding the pET28a Plasmid Map: Your Ultimate Guide
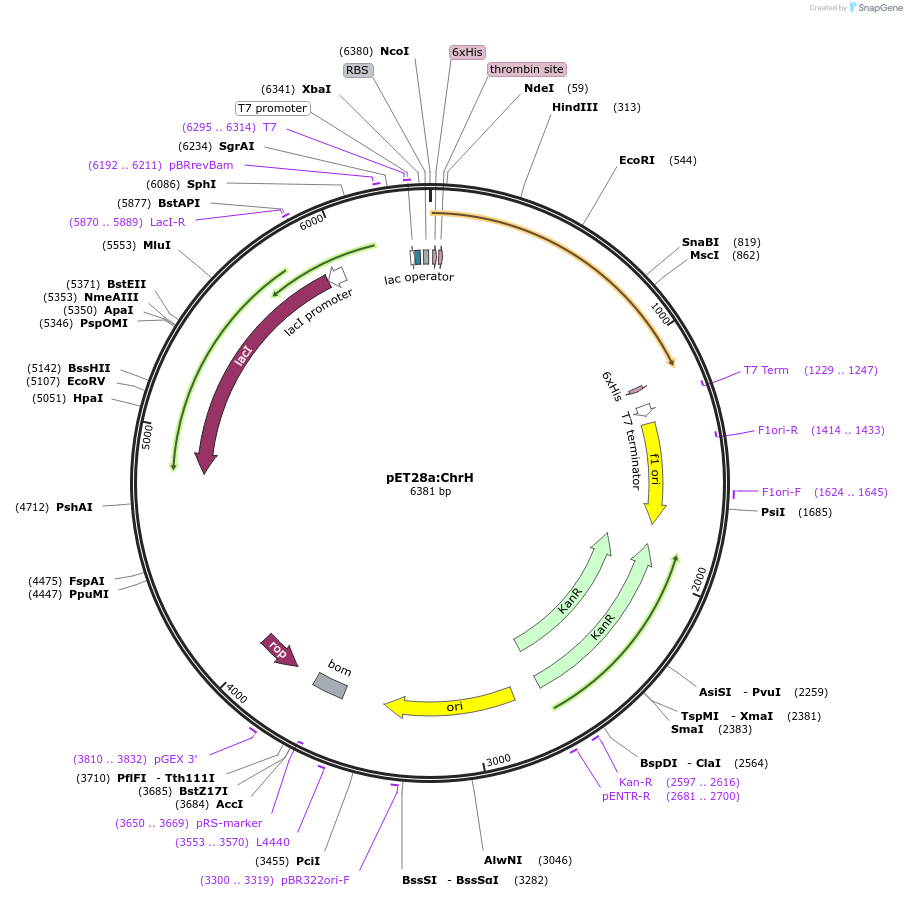
The pET28a plasmid map represents a vital tool in modern molecular biology, empowering researchers to produce specific proteins in bacterial systems. This bacterial expression vector, widely known as pET28a plasmid map, is a workhorse for expressing recombinant proteins, allowing scientists to create large quantities of target proteins for study and application. Knowing the intricacies of its structure, including key elements like the T7 promoter and the His-tag, is fundamental for anyone looking to successfully navigate protein expression experiments today.
What is the pET28a Plasmid Map and Why is it Essential?
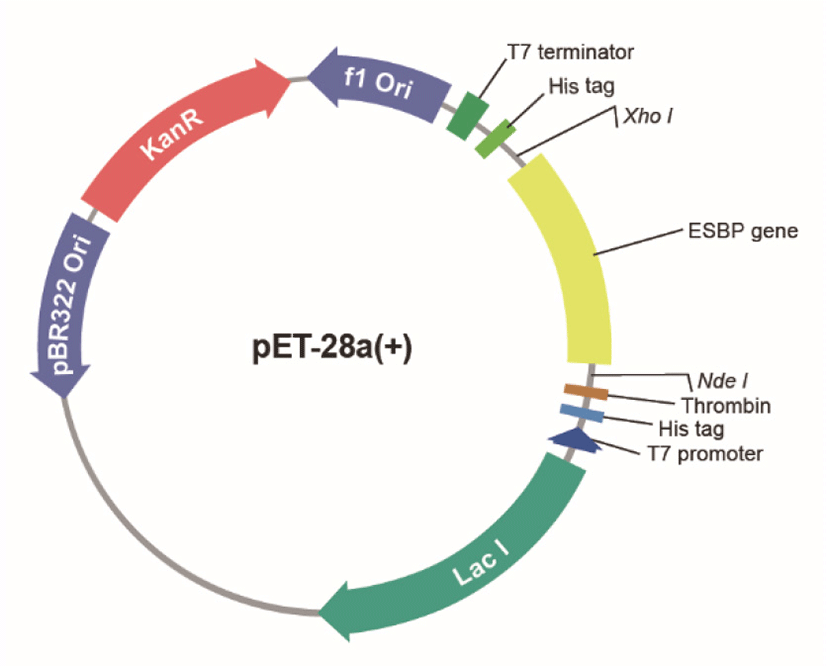
The pET28a plasmid map is a popular expression vector used primarily in Escherichia coli (E coli) for high-level production of recombinant proteins. It serves as a genetic vehicle, carrying the DNA sequence for a protein of interest into a bacterial cell, where the cell's machinery is then hijacked to synthesize that specific protein. The pET28a plasmid map is indispensable because it offers a highly efficient and well-characterized system for inducing gene expression and purifying the resulting protein, making it a cornerstone for biochemical and biotechnological research.
The Power of the pET28a Plasmid Map in Protein Production
Imagine you need to study a particular protein in great detail. The pET28a plasmid map makes it possible to produce that protein in significant amounts. This is achieved by carefully designed genetic elements within the pET28a plasmid map, which direct the bacterial cell to transcribe and translate your gene of interest. Researchers depend on the pET28a plasmid map for everything from enzyme production to structural biology studies, proving its versatility and reliability in the lab.
Key Features of the pET28a Plasmid Map You Need to Know
Understanding the individual components within the pET28a plasmid map is crucial for effective cloning and expression. Each part plays a specific role, contributing to the overall functionality of this powerful expression system. Let's explore the standout features of the pET28a plasmid map that make it so effective.
The T7 Promoter and lac Operator of the pET28a Plasmid Map
At the heart of the pET28a plasmid map's expression system lies the strong T7 promoter. This promoter is recognized by the T7 RNA polymerase, an enzyme often supplied by the host E coli strain itself, leading to very high levels of transcription. Coupled with the T7 promoter is a lac operator, which provides tight regulation of gene expression. This tight control ensures that your target protein is only produced when induced, typically with IPTG, minimizing any potential toxicity to the host cell and optimizing protein yield with the pET28a plasmid map.
His-tag for Efficient Purification in the pET28a Plasmid Map
One of the most user-friendly features of the pET28a plasmid map is the inclusion of an N-terminal His-tag (6xHistidine tag). This short sequence encodes six histidine residues that bind strongly to metal ions like nickel or cobalt. This allows for straightforward and highly efficient purification of the recombinant protein using Immobilized Metal Affinity Chromatography (IMAC), a massive advantage when working with the pET28a plasmid map.
Selectable Marker and Origin of Replication in the pET28a Plasmid Map
To ensure that only bacteria containing the pET28a plasmid map survive and multiply, the vector includes a selectable marker, specifically the kanamycin resistance gene. This gene confers resistance to the antibiotic kanamycin, allowing for selection on antibiotic-containing media. Additionally, the pET28a plasmid map contains a ColE1 origin of replication, which dictates the plasmid's copy number within the bacterial cell, typically maintaining a high copy number for robust protein production.
How to Use the pET28a Plasmid Map for Your Experiments
Embarking on a protein expression project with the pET28a plasmid map involves several key steps. From inserting your gene to inducing expression, each stage is vital for successful outcomes. With a clear understanding of the pET28a plasmid map, you can confidently navigate these steps.
Cloning Your Gene into the pET28a Plasmid Map
The first step involves cloning your gene of interest into the multiple cloning site (MCS) of the pET28a plasmid map. This region is strategically located downstream of the T7 promoter and His-tag, ensuring proper fusion and expression. Using restriction enzymes and ligase, you insert your DNA sequence, creating a recombinant pET28a plasmid map ready for transformation.
Transformation and Selection with the pET28a Plasmid Map
Once your gene is ligated into the pET28a plasmid map, the plasmid is introduced into a suitable E coli host strain, often those engineered to carry the T7 RNA polymerase gene, like BL21(DE3) cells. This process is called transformation. The transformed cells are then plated on agar containing kanamycin, selecting only those bacteria that have successfully taken up the pET28a plasmid map.
Induction of Protein Expression Using the pET28a Plasmid Map
After selecting your positive clones, protein expression is induced. This typically involves adding IPTG to the bacterial culture. IPTG de-represses the lac operator, allowing the T7 RNA polymerase to bind to the T7 promoter on the pET28a plasmid map and initiate transcription of your target gene. This leads to the rapid and high-level synthesis of your desired protein.
What Others Are Asking? (FAQ style) about the pET28a Plasmid Map
What is pET28a plasmid map used for?
The pET28a plasmid map is primarily used as an expression vector for producing recombinant proteins in bacterial systems, specifically E coli. It allows researchers to express genes of interest at high levels, often with an N-terminal His-tag for simplified purification, making it a staple in molecular biology for protein production and study.
What are the features of pET28a plasmid map?
Key features of the pET28a plasmid map include a strong T7 promoter for inducible high-level expression, a lac operator for transcriptional control, an N-terminal His-tag for affinity purification, and a kanamycin resistance gene for antibiotic selection. It also contains a multiple cloning site for gene insertion and a ColE1 origin of replication.
How does pET28a induce protein expression?
Protein expression with the pET28a plasmid map is induced by adding IPTG. IPTG acts as an allosteric effector, binding to and inactivating the lac repressor protein. This de-represses the lac operator, allowing T7 RNA polymerase (supplied by the host cell) to bind to the T7 promoter and initiate transcription of the cloned gene, leading to protein synthesis.
What is the origin of replication in pET28a plasmid map?
The pET28a plasmid map contains a ColE1 origin of replication. This origin dictates how the plasmid replicates independently within the host bacterial cell, influencing its copy number. The ColE1 origin typically leads to a relatively high copy number, which is beneficial for maximizing the yield of the target protein.
What is the selectable marker in pET28a plasmid map?
The selectable marker in the pET28a plasmid map is the kanamycin resistance gene. This gene encodes an enzyme that inactivates the antibiotic kanamycin, allowing only bacteria that have successfully incorporated the pET28a plasmid map to grow in the presence of kanamycin, thus facilitating easy selection of transformants.
What is the size of pET28a plasmid map?
The pET28a plasmid map typically has a size of approximately 5369 base pairs (bp). This size is relatively standard for an expression vector, providing enough genetic information for its functional elements while remaining manageable for cloning and manipulation in laboratory settings for protein expression experiments.
FAQ about the pET28a Plasmid Map
What is the pET28a plasmid map?
The pET28a plasmid map is a bacterial expression vector, a small circular DNA molecule, used to produce target proteins in E coli. It's engineered for high-level, inducible protein synthesis, making it invaluable for researchers.
Who uses the pET28a plasmid map?
Molecular biologists, biochemists, and biotechnology researchers widely use the pET28a plasmid map. Anyone needing to produce large quantities of a specific protein for study, therapeutics, or industrial applications relies on this vector.
Why is the pET28a plasmid map effective?
The pET28a plasmid map is effective due to its strong T7 promoter for high expression, a regulatable lac operator, and an N-terminal His-tag that simplifies protein purification, significantly streamlining the protein production workflow.
How is the pET28a plasmid map utilized?
Researchers utilize the pET28a plasmid map by cloning their gene of interest into its multiple cloning site. They then transform this recombinant plasmid into E coli, induce protein expression with IPTG, and finally purify the His-tagged protein.
Summary of Key Insights on the pET28a Plasmid Map
The pET28a plasmid map is undeniably a cornerstone in recombinant protein expression. Its ingenious design, featuring a powerful T7 promoter, precise lac operator control, and an invaluable His-tag for purification, simplifies the complex task of protein production. Whether you're a seasoned researcher or just starting in molecular biology, understanding the pET28a plasmid map empowers you to achieve robust protein yields efficiently. This tool continues to drive innovation, enabling deeper insights into biological processes and paving the way for new biotechnological advancements. Mastering the pET28a plasmid map truly equips you for success in the dynamic world of protein science.
pET28a plasmid map is a critical tool for recombinant protein expression. It features a T7 promoter for high-level expression, a His-tag for purification, and kanamycin resistance for selection. This vector is widely used in E coli systems for producing target proteins efficiently in molecular biology research.
Figure 2 Mapping Of PET28a His Plasmid Figure 2 Engineering Success Shanghai United IGEM 2022 T Shanghai United Addgene PET28a PA1472 Cterm His 220485 Map Q85 Autocrop
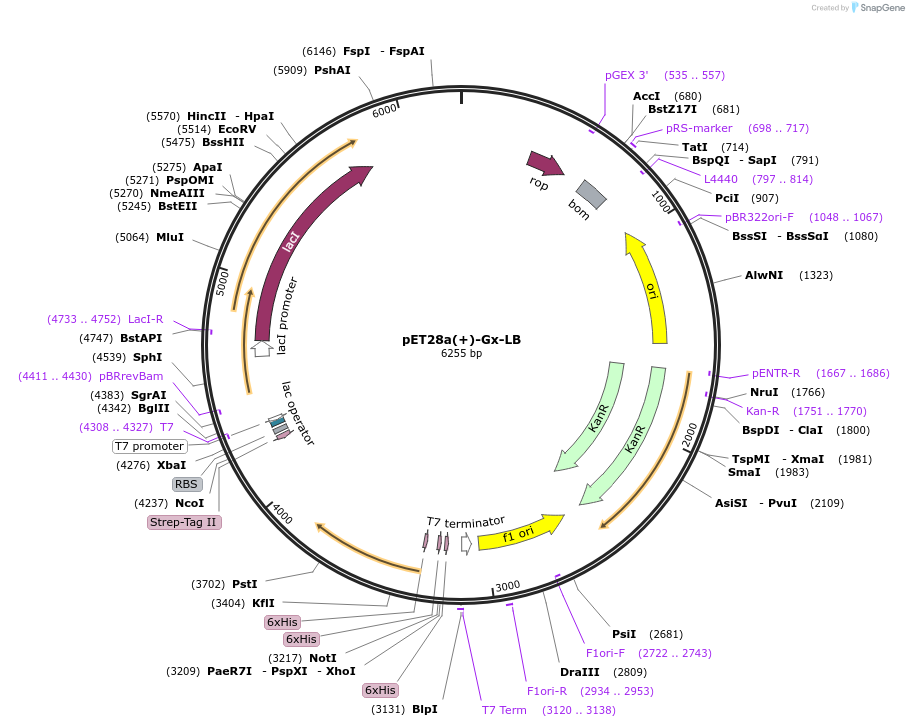
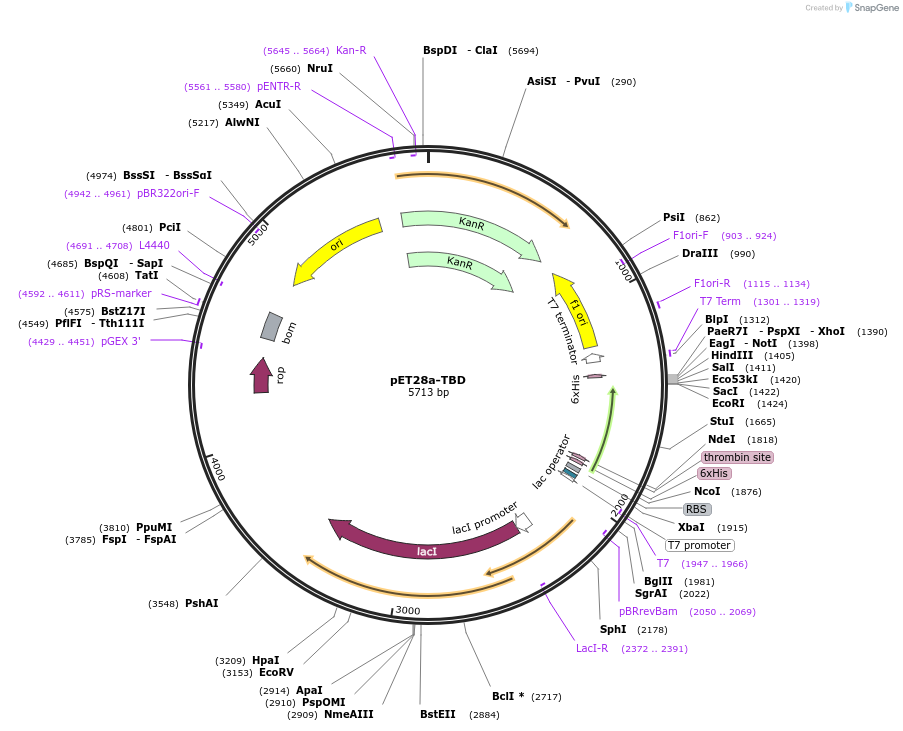
Addgene PET28a TBD Addgene Plasmid 236737 Sequence 471112 Map Addgene PET28a Gx LB Addgene Plasmid 220126 Sequence 437697 Map Figure 16 Plasmid Map Of PET28a Transferrin MCherry T19 Addgene 6his WT GusA PET28a 61156 Map
Addgene PET28a PA1377 Nterm His Addgene Plasmid 220481 Sequence 434036 Map Plasmid Maps Of A PET28A And B PFM23 Both Plasmids Harbour A A Plasmid Maps Of A PET28A And B PFM23 Both Plasmids Harbour A A PMB1 Origin Of.ppmAddgene PET28a T7 ARG1 106473 Map Figure 10 Plasmid Map Of PET28a Transferrin T16
Food Science Of Animal Resources Kosfa 39 4 601 G1 Addgene PET28a EgC A93347b0 Af62 11e0 90fe Addgene PET28a SpeG Nterm His Addgene Plasmid 220478 Sequence 434034 Map PET 28a Sequence And Map PET 28a( )
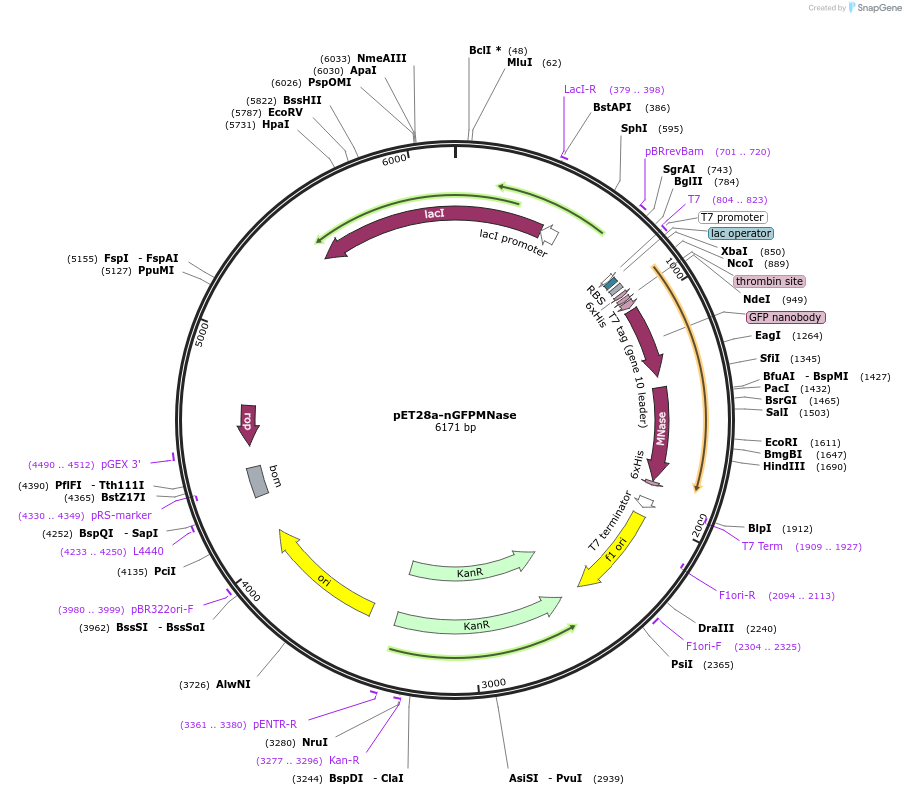
Addgene PET28a NGFPMNase Addgene Plasmid 187826 Sequence 376981 Map Addgene PZH82 PET28a Rai1 Addgene Plasmid 231651 Sequence 462321 Map Description Shanghai United IGEM 2022 T Shanghai United Addgene PET28a FbGH30 86463 Map Q85 Autocrop
Addgene PET28a LIC 5d03c2b0 Af63 11e0 90fe .848x848 Q85 Autocrop Figure 7 Mapping Of PET28a His MS18 Plasmid Figure 7 Addgene PET28a PA1472 Nterm His Addgene Plasmid 220480 Sequence 434035 Map Addgene PET28a MinC 133628 Map .848x848 Q85 Autocrop
Addgene PET28a His6 GFP UROD Addgene Plasmid 236741 Sequence 469915 Map Addgene PET28a HsSENP3 Addgene Plasmid 71467 Sequence 129183 Map Addgene PET28a DONSON S437A 208803 Map I8K6MjLCtl0 JcOE Addgene PET28a ChrH Addgene Plasmid 225084 Sequence 447349 Map
Addgene PET28a TS2126 RnlA Strep Addgene Plasmid 159350 Sequence 324518 Map Addgene PET28a PAN 200971 Map DhV Addgene PET28a AzaM 224428 Map Addgene PET28a AzaC 224424 Map
Addgene PET28a Cas9 Cys 53261 Map UxX Q85 Autocrop Addgene PET28a NGFPMNase 187826 Map Addgene PET28a TrxC Addgene Plasmid 225742 Sequence 450365 Map The Map Of PET 28a As An Expression Vector Novagen Cat No 69337 3 The Map Of PET 28a As An Expression Vector Novagen Cat No 69337 3 L1 Gene Was


/pET-28a(+)/pET-28a(+).png)