Have you ever wondered why some taxes feel heavier for certain people than others? Many Americans often ask, What is a regressive tax? and more importantly, How does it truly affect my everyday finances and the broader economy? This in-depth article will explain what is regressive tax, exploring its definition, common examples, and why it’s a trending topic in discussions about economic fairness and public policy across the United States. We will dive into who pays these taxes, what makes them regressive, when they typically apply, where they are most noticeable in your daily life, why they generate so much debate, and how they shape income inequality. Discover practical insights into how these tax structures work and empower yourself with knowledge to better understand their influence on your financial well-being, helping you navigate the complexities of tax systems and champion for fair economic solutions. This comprehensive guide serves as an invaluable resource for anyone seeking clarity on this critical economic concept.
When people ponder their financial contributions to society, a frequent question that pops up is, What exactly is a regressive tax, and how does it play a role in my household budget? You see, understanding these tax systems can truly empower you to grasp the bigger picture of economic fairness. This type of tax disproportionately affects individuals with lower incomes, meaning it takes a larger percentage of their earnings compared to those who earn more. Why is this distinction so crucial, you might ask? Well, its about how the tax burden is distributed across different income brackets, directly influencing economic disparities. Who does this kind of tax really impact the most, and how does it work in practice? Well explore when and where these taxes appear, why they often spark significant debate, and how recognizing them can help you better navigate your financial landscape and even advocate for change. This deep dive aims to demystify regressive taxation, providing you with clear insights into its mechanisms and broader societal implications.
Understanding What is Regressive Tax: A Core Definition
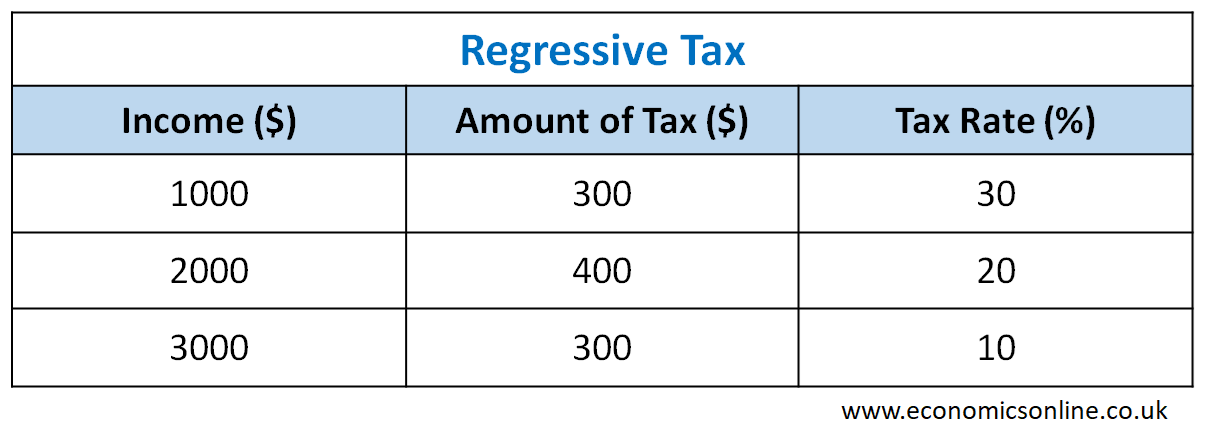
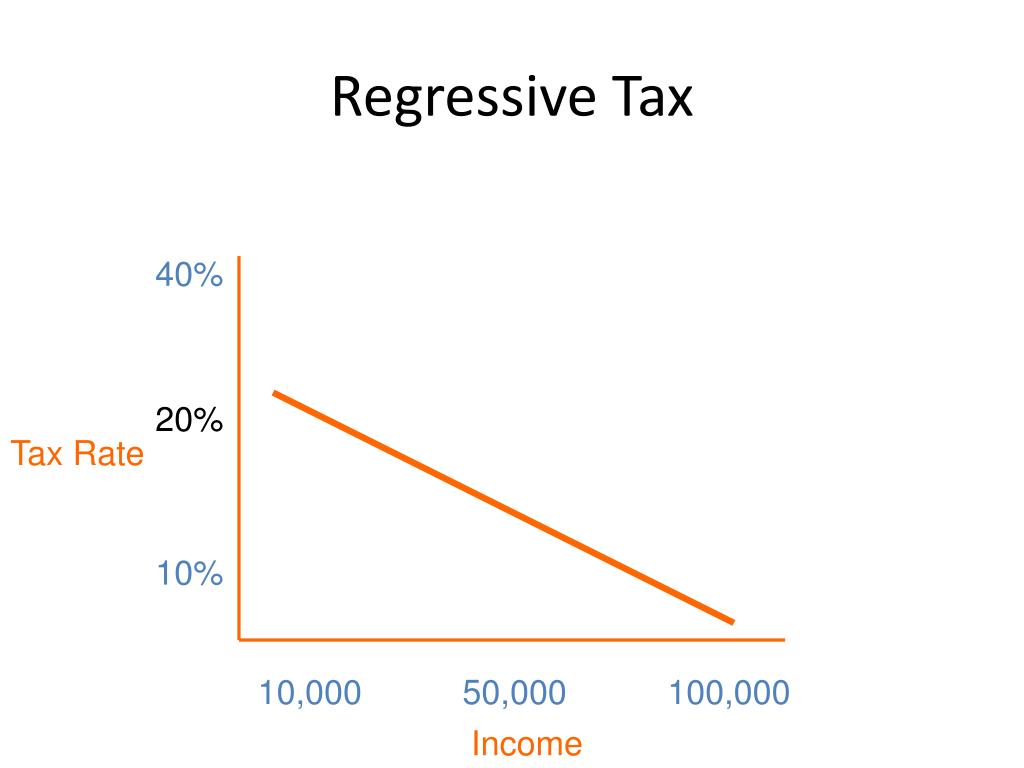
Lets get straight to the heart of the matter: what is regressive tax? Simply put, a regressive tax is a tax where the average tax rate decreases as the taxpayers income increases. This means that people earning less money end up paying a larger proportion of their income in taxes than those earning more. Why does this happen? Often, these taxes are levied on goods, services, or assets, and everyone pays the same dollar amount, regardless of their financial capacity. When does this become an issue? It becomes a pressing concern when we consider its implications for economic equality and the financial strain on struggling families. Where can you find these taxes? They are deeply embedded in our daily lives, from the items we purchase at the grocery store to the gasoline we put in our cars. How do these taxes contrast with other forms of taxation, like progressive taxes, which actually increase with income? Understanding this contrast is key to appreciating why regressive taxes frequently become a focal point in discussions about fairness and equity in tax policy across the United States.
How Does Regressive Tax Work? The Mechanics Explained
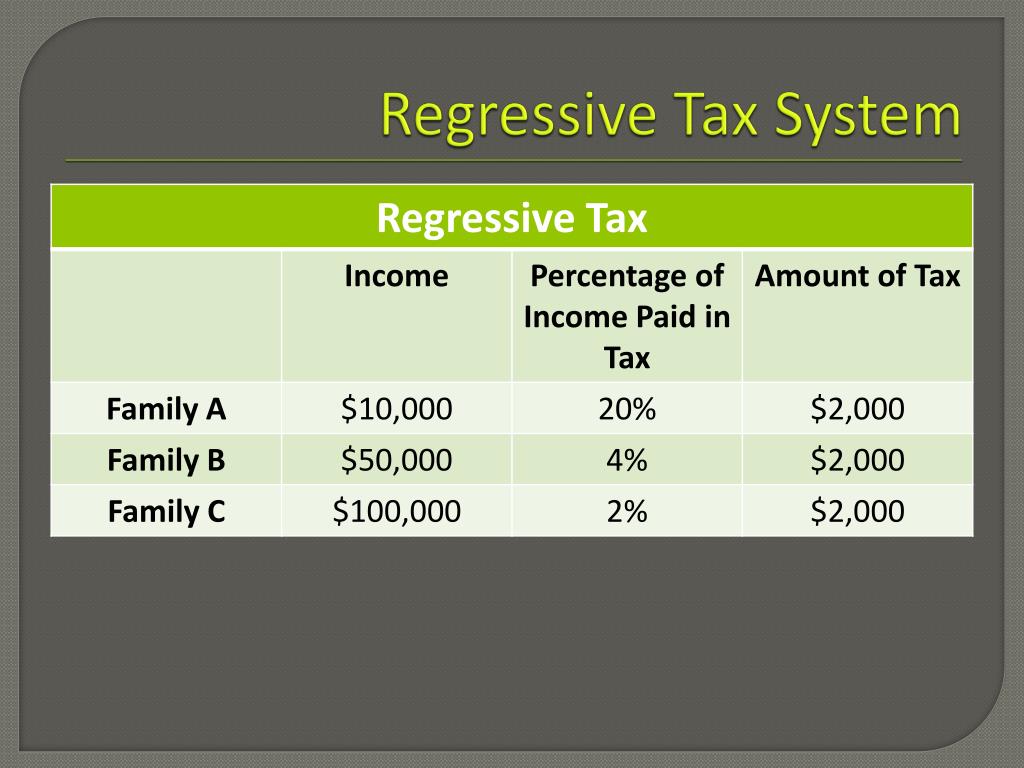
So, how does a regressive tax actually operate in the real world, and what makes it truly regressive? Imagine a sales tax of 7% on all goods. If someone with a lower income spends nearly all their money on necessities, like food and clothes, that 7% sales tax eats up a significant portion of their total earnings. For example, if a person earns $20,000 a year and spends $15,000 on taxable items, they pay $1,050 in sales tax. Thats 5.25% of their total income. Now, consider someone earning $200,000 who also spends $15,000 on taxable items; they still pay $1,050 in sales tax, but for them, its a mere 0.525% of their income. This stark difference in the percentage of income paid reveals the regressive nature. Who is truly affected by this? Its primarily those with less disposable income, as they spend a larger percentage of their earnings on items subject to these flat-rate taxes. When do these taxes hit hardest? They hit hardest during periods of inflation or economic hardship, where every dollar counts even more for those on tight budgets. This mechanism underscores why understanding what is regressive tax is so vital for citizens and policymakers alike.
Why Are Regressive Taxes a Concern for Many?
Why do regressive taxes spark such passionate debates and concern among economists, policymakers, and everyday citizens alike? The fundamental issue lies in their impact on income inequality. When taxes disproportionately affect lower-income individuals, it widens the gap between the rich and the poor, making it harder for those at the bottom to build wealth and improve their financial standing. How does this happen? By taking a larger slice of their limited income, regressive taxes reduce their ability to save, invest, or spend on other essential needs, perpetuating a cycle of economic struggle. Who ultimately bears the heaviest load? It is often the working poor, the elderly on fixed incomes, and marginalized communities. When does this become a major societal problem? It becomes a problem when a significant portion of the population faces increased financial pressure, which can lead to social unrest and hinder overall economic growth. Where do we see the evidence of this concern most vividly? In public discourse, legislative debates, and advocacy group efforts pushing for more equitable tax reforms. Recognizing what is regressive tax empowers us to question existing structures and advocate for policies that foster greater economic justice for everyone.
Common Examples of What is Regressive Tax in Action
When we talk about what is regressive tax, it’s helpful to look at real-world examples that you might encounter every single day. The most common illustration is the sales tax. When you buy groceries, clothes, or electronics, you pay a sales tax, which is a fixed percentage of the item’s price. As we discussed, a person earning minimum wage pays the same dollar amount in sales tax on a $20 shirt as a millionaire buying the exact same shirt. For the minimum wage earner, that tax represents a much larger portion of their daily or weekly earnings. Another common example includes sin taxes on items like tobacco, alcohol, and sometimes sugary drinks. While these taxes aim to discourage consumption of certain products, they tend to affect lower-income individuals more, as these groups often spend a higher percentage of their income on such items, whether for necessity or addiction. What about property taxes? While property taxes are typically considered progressive (because wealthier people own more expensive homes), renters often experience an indirect regressive effect, as landlords may pass on property tax costs through higher rents, impacting those with less income disproportionately. User fees for public services, like vehicle registration fees or tolls, also exhibit regressive qualities because everyone pays the same flat fee regardless of their income. Where do these examples manifest most clearly? In virtually every state across the US, influencing countless transactions daily. Understanding these common examples truly highlights the broad reach and impact of regressive taxation on diverse populations.
| Key Aspect | Description of What is Regressive Tax |
|---|---|
| Definition | A tax that takes a larger percentage of income from low-income earners than from high-income earners. |
| Impact on Income | Disproportionately burdens individuals with less disposable income, reducing their purchasing power and savings capacity. |
| Common Examples | Sales tax, sin taxes (tobacco, alcohol), flat user fees, and some forms of property tax (indirectly for renters). |
| Economic Effect | Can exacerbate income inequality by placing a heavier tax burden on those who can least afford it. |
| Policy Debate | Often at the center of discussions regarding fairness, equity, and the design of a just tax system. |
The Debate Around What is Regressive Tax: Pros and Cons
The concept of what is regressive tax doesnt exist in a vacuum; it’s a constant subject of debate. On one hand, proponents argue for their simplicity and efficiency in revenue generation. Why might some argue for them? They are often easier to implement and administer compared to complex income-based tax systems. Everyone pays the same rate or amount, making collection straightforward and potentially lowering administrative costs. When do these arguments hold most weight? Often, when a government needs to raise broad revenue for public services quickly and effectively without complicated income assessments. Who benefits from this simplicity? Governments seeking stable revenue streams, as consumer spending tends to be less volatile than income. However, the strong arguments against regressive taxes primarily focus on fairness and economic equity. Critics vehemently point out how these taxes disproportionately burden low-income households, increasing financial stress and widening income gaps. How can we truly ensure a fair society if the tax system places a greater percentage burden on those least able to afford it? This fundamental question underscores the core of the debate, highlighting a tension between practical revenue collection and ethical distribution of financial responsibility. Understanding both sides helps us engage thoughtfully with proposals for tax reform and appreciate the nuanced challenges involved in crafting a truly equitable system.
Navigating the Impact of What is Regressive Tax on Your Wallet
Now that weve explored what is regressive tax and its mechanics, how can you navigate its impact on your own financial situation and even empower yourself to influence change? Awareness truly is the first step. By recognizing which taxes are regressive, you can make more informed spending decisions. For instance, being mindful of sales tax when making significant purchases, or understanding how gas prices and associated taxes affect your transportation budget. Who can you turn to for more information or assistance? Financial advisors, consumer advocacy groups, and government resources often provide valuable insights into managing your money effectively within the existing tax structure. When it comes to influencing change, why not engage with local and national policy discussions? Many states offer various exemptions or rebates to help mitigate the regressive nature of certain taxes for lower-income families, such as sales tax holidays on specific necessities or property tax relief programs. Where can you make your voice heard? Contacting your elected officials, participating in community forums, or supporting organizations that advocate for progressive tax reforms are powerful ways to contribute. Remember, your active participation in understanding and advocating for a more equitable tax system can genuinely make a difference. Empower yourself by staying informed and taking action!
People Also Ask About What is Regressive Tax:
Q: What is a regressive tax, simply put? A: A regressive tax takes a larger percentage of income from low-income individuals than from high-income individuals. Everyone pays the same amount or rate, but its impact on a lower income is proportionally greater.
Q: What are common examples of regressive taxes in the US? A: Sales taxes, sin taxes on items like tobacco and alcohol, and certain flat user fees are common examples of regressive taxes in the United States.
Q: Why is understanding what is regressive tax important? A: Understanding regressive tax is important because it helps you see how tax policies affect economic inequality and your personal finances, empowering you to make informed decisions and advocate for fairer systems.
Q: How does a regressive tax differ from a progressive tax? A: A regressive tax takes a smaller percentage of income as income rises, while a progressive tax takes a larger percentage of income as income rises. Income tax is typically progressive, whereas sales tax is regressive.
Q: What measures can mitigate the impact of regressive taxes? A: Measures like tax credits for low-income families, exemptions for essential goods from sales tax, or targeted assistance programs can help mitigate the regressive impact of certain taxes.
Keywords: what is regressive tax, regressive tax examples, sales tax, sin tax, economic inequality, tax fairness, tax policy, progressive tax, flat tax, income distribution, US taxation, consumer tax, tax impact, financial literacy
A regressive tax disproportionately burdens lower-income individuals; common examples include sales tax and sin taxes; understanding what is regressive tax reveals its impact on economic inequality; these taxes take a larger percentage of income from those who earn less; they are a significant part of the ongoing debate about tax fairness and income distribution; awareness helps citizens advocate for more equitable tax policies.
Regressive Taxes 2 6.webpRegressive Tax Examples Pros Cons How To Calculate Rt1 Regressive Tax PPTX Regressive Tax 3 2048
Sales Tax Is An Example Of A Regressive Tax At Justin Northcote Blog Regressive Tax Regressive Taxes 3 6.webpPPT TAXES PowerPoint Free Download ID 2556010 Regressive Tax2 L What Is A Regressive Tax System Why Does It Affect How Regressive Taxes Work.webp
PPT TAXES PowerPoint Free Download ID 2556010 Regressive Tax1 L What Is Regressive Tax PPTX What Is Regressive Tax 1 2048 ACCTG310 505051 Graphics ACCTG310 Carmen L1G3 What Is A Regressive Tax System Why Does It Affect Common Types Of Regressive Taxes.webp
PPT Taxes PowerPoint Free Download ID Regressive Tax L Regressive Tax TaxEDU Glossary Nearly Half The States Require To File Income Taxes After Single Day Of Work Nbsp 1132x1536 PPT TAXES PowerPoint Free Download ID 2556010 Regressive Tax L Regressive Tax Definition Pros Cons Examples Regressive Tax Definition .webp
PPT TAXATION PowerPoint Free Download ID Regressive Tax Example L Regressive Tax How A Regressive Tax System Works Regressive Tax PPT TAXES The Main Source Of Government Revenue PowerPoint Regressive Tax L Regressive Tax System Definition Examples Pros Criticisms Criticisms And Advantages Of Regressive Tax System
What Is Regressive Tax PPTX What Is Regressive Tax 4 2048 Regressive Tax Examples Top 4 Examples Of Regressive Tax Explained Regressive Tax Examples Regressive Tax Blog Card PPT PB202 PowerPoint Free Download ID Regressive Tax L
Regressive Tax Key Examples And Impacts Regressive Tax Key Examples And Impacts10 Regressive Tax Stock Photos Pictures Royalty Free Images IStock Tax Structure For Regressive And And Progressive Tax Rate Regressive Tax Definition Types How This System Work .webpAndrew Yang S Book Report Patrick Ruff Regressive Tax
Regressive Taxes Definition Common Types Final PPT American Tax System PowerPoint Free Download ID Regressive Tax System L Regressive Tax Policy Structure Calculation Regressive Decoding The 2025 Brazilian Income Tax Landscape A Guide Regressive Tax
What Is A Regressive Tax System Why Does It Affect What Is A Regressive Tax System Why Does It Affect Lower Income Earners 1.webpAfter Decades Of Costly Regressive And Ineffective Tax Cuts A New 5 17 23tax Testimony F3

:max_bytes(150000):strip_icc()/regressivetax.asp-final-28ca4ccf48fa48689f0907c7db951496.png)